- Google blocked nearly 2 million malicious or rule-breaking apps before they reached the Play Store in 2025.
- Artificial intelligence made it possible to strengthen controls, detect fraud patterns, and analyze billions of applications daily.
- Play Protect extended protection beyond the official store, monitoring external apps and new forms of fraud.
- Access to sensitive data was tightened and fake reviews were combated to improve user trust in Spain and Europe.

The latest security assessment of the Android ecosystem leaves one headline unequivocal: In 2025, Google blocked the arrival of nearly 2 million malicious or policy-violating apps. before they were published on the Play Store. Behind this figure is a combination of automated controls, human review, and, above all, the intensive use of artificial intelligence models.
For users of Spain and the rest of EuropeThis reinforcement is not a minor issue. Mobile phones have become the primary device for online banking, shopping, dealings with government agencies, and messaging, and any security breach can have serious consequences. economic fraud, data theft, or identity theftGoogle says its goal is to maintain a balance: making life increasingly difficult for cybercriminals without blocking innovation from legitimate developers.
A record year: almost 2 million apps stopped at the door
According to the report on how ecosystems have been kept safe Google Play and Android during 2025The company prevented the publication of more than 1,75 million apps that violated its rulesIn other words, they were stopped before they were even available to a single user.
Many of these apps were linked to attempts to install malware, such as Sparkkitty malware on mobile devicesFinancial fraud, hidden subscriptions, or abusive collection of personal data are among the issues Google addresses. Google's stated priority is that apps do not cause real harm or jeopardize users' privacy or finances.
In addition to blocking specific applications, the company cleaned up the developer environment. Throughout 2025, They closed more than 80.000 accounts associated with malicious activitywhether it was by uploading harmful apps, trying to bypass store filters, or repeatedly engaging in suspicious behavior.
Another important front was that of applications that, without necessarily being malware, attempted access more data than necessaryGoogle Play prevented that from happening around 255.000 apps obtained excessive permissions over confidential informationsuch as precise location, contacts, or call logs.
At the same time, the company points out that every new app undergoes a thorough review: over 10.000 automatic security checks per applicationThese analyses examine the code, the use of sensitive permissions, and potential attempts to obfuscate suspicious behavior. The underlying message is clear: sneaking a dangerous app through the front door is becoming increasingly difficult.
AI, a key tool for detecting fraud and sophisticated malware
The report highlights that one of the major developments of 2025 has been the integration of advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning models in review processesThese systems are used both in the Play Store and in the internal security layers of Android.
Cybercriminals are also now using AI to refine their attacks, making the cat-and-mouse game more complex. In response, Google has begun using Generative AI to help human reviewers identify hard-to-detect malicious patterns, such as malware that remains inactive for several days after installation or apps that change behavior through silent updates.
Instead of simply comparing files against a database of known threats, these models analyze behaviors, data flows, use of permissions, and connections to external serversIf they detect suspicious combinations—for example, a flashlight app requesting access to SMS and contacts—the application is blocked or sent for further manual analysis.
This AI layer is also used to monitor the commercial part of the ecosystem: reviews, ratings, and usage patternsMany digital scams rely on fake reviews to gain credibility, so the automatic detection of anomalous behavior in ratings has become as important as code analysis.
Google insists that AI does not completely replace the human security teamHowever, it does filter and categorize the enormous volume of applications uploaded each year, allowing attention to be focused on the most complex cases. In an environment with millions of active apps, this type of automation is practically the only way to keep up.
Play Protect: the shield that watches over you inside and outside the Play Store

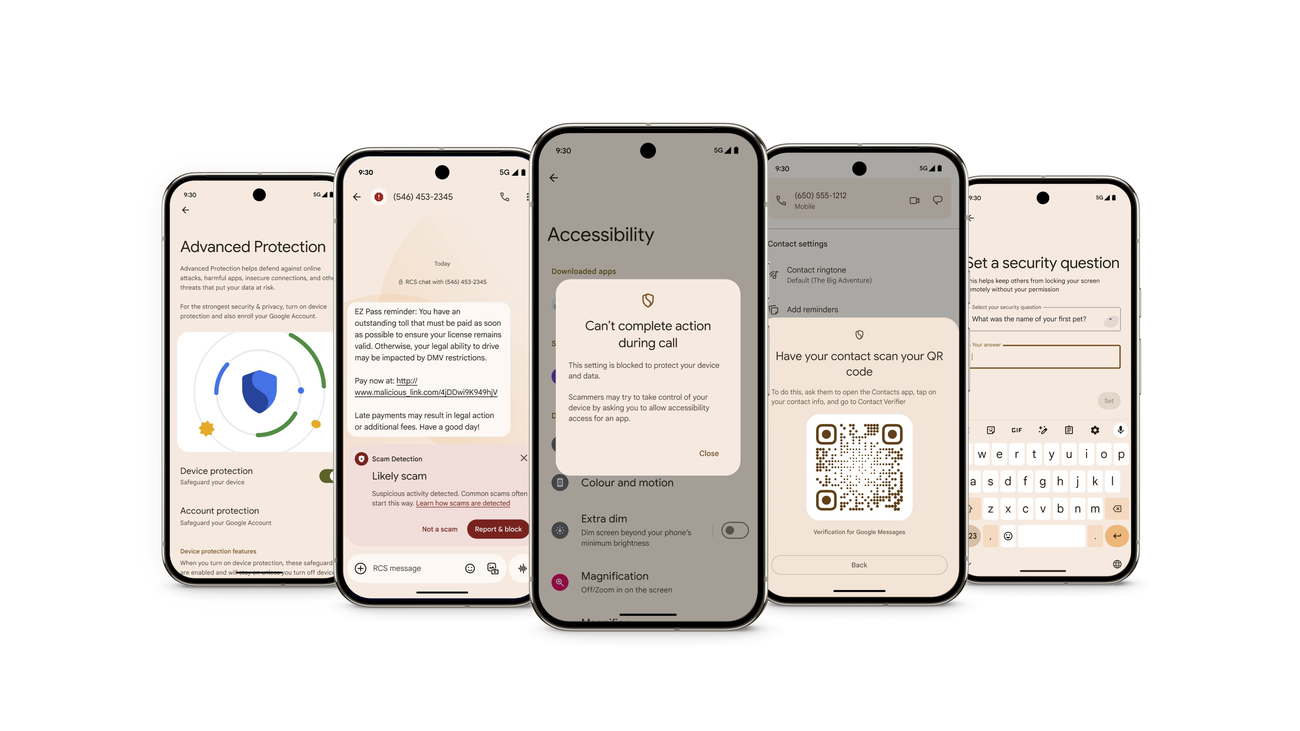
Beyond the official store, the main focus of the report is Google Play ProtectThe protection system integrated into most Android devices. This service continuously analyzes both applications downloaded from the Play Store and those received from other sources. external sources through APK files.
In 2025, Play Protect It analyzed more than 350.000 billion applications per day.This figure includes downloads, updates, and already installed apps. Based on these analyses, the system It identified tens of millions of malicious applications distributed outside the official store.blocking its installation or warning the user when it detected risky behavior, in addition to offering resources protection guide.
The rise of downloads from websites, third-party stores, or links shared on social networks and messaging apps This is one of the company's main concerns. Many users disable, even temporarily, the restrictions on installation from unknown sources, which opens a perfect door for attackers looking to bypass Play Store filters. To identify these practices, it's also advisable to review alarm signals that indicate infection or abnormal behavior in the device.
To reduce that risk, the latest versions of Android incorporate measures such as temporary isolation of apps installed from outside the store until Play Protect finishes its scan, which helps locate hidden applications and assess its potential danger. If anything unusual is detected, the system can prevent the application from running or drastically limit its access to sensitive data.
The protection doesn't stop at software alone: Google has extended the capabilities of Play Protect to encompass New forms of fraud, such as certain telephone scams and phishing campaigns targeting mobile usersAccording to the company, this broad approach is necessary because attackers are increasingly combining different channels—apps, calls, SMS, social media—in a single operation; that's why guides are also being developed for detect if a hacker has accessed your phone.
Personal data, fake reviews, and user trust
One of the key aspects of the report is the management of the personal dataThroughout 2025, Google has strengthened the rules governing what information an application can request and for what purpose, aligning itself with regulatory requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
In practice, this has meant that Hundreds of thousands of apps have had their access to information considered sensitive restricted.Among them were more than 255.000 companies that attempted to obtain excessive permissions. Many have had to adapt their operations to new privacy APIs that, by design, limit the ability to track users or build detailed profiles without their consent.
Another key front has been that of the manipulated reviews and ratingsGoogle's automated detection systems blocked more than 2025 160 million reviews and ratings categorized as spam or fraud, both those aimed at inflating the rating of dubious apps and coordinated campaigns to sink the competition.
According to figures shared by the company, this cleaning work prevented an average drop of around half a point in the rating of many legitimate applicationswhose reputations would have been damaged by organized attacks. In markets like Spain, where other users' opinions carry significant weight when deciding whether or not to install an app, these kinds of measures have a direct impact on trust.
In parallel, Google has promoted initiatives such as external security assessment programs for apps in critical sectors —banking, utilities, healthcare—, which may display additional verification labels. Although these badges are not yet widespread, they are intended as an extra tool for users to more easily identify which applications have undergone more thorough audits.
Fewer malicious accounts and a somewhat cleaner ecosystem
The report also points to a striking trend: The number of malicious developer accounts suspended has decreased compared to previous years., reaching just over 80.000 during 2025. Far from interpreting it as a relaxation of controls, Google presents it as a sign that its new barriers to entry are working.
These barriers include the enhanced identity verification for developersMore detailed reporting requirements regarding data usage, as well as compliance tools that are directly integrated into development workflows. In other words, the aim is to curb suspicious behavior long before an app even reaches the review stage.
For legitimate developers, especially in Europe, these measures mean that Security and privacy are no longer optional extras and become part of the application design from the outset. Using only essential permissions, clearly explaining what data is collected, and subjecting the code to automated analysis have become crucial to avoid delays or rejections during publication.
At the same time, Google claims it is trying do not turn the publishing process into an insurmountable obstacle For small studios or startups. Assistants and tools have been introduced that indicate, step by step, what changes are necessary to comply with the regulations, with the aim of reconciling an open ecosystem with a reasonable level of risk.
From the users' point of view, the expected consequence is that Downloading an app from the Play Store remains, in general terms, a safe act. without needing to be a cybersecurity expert. The risk is never zero, but the bar for those trying to sneak in dangerous software is getting higher all the time.
Android under constant pressure and the bet on the future
The figures collected by Google show the extent to which Android continues to be a prime target for cybercriminalsThe enormous number of devices in circulation—including millions in Spain and the rest of the European Union—turns any vulnerability into a business opportunity for attackers.
To cope with this pressure, the company is relying on the same tools used by bad actors: automation, big data analytics and artificial intelligenceThe difference, they argue, is the volume of signals they can process and the ability to detect new variations of known threats, even when the code changes.
Looking ahead to the coming months, Google anticipates that it will continue Strengthening Play Protect, expanding external audits, and reviewing its permissions and access policies for sensitive dataIt also aims to further integrate compliance tools into development platforms, so that many violations are corrected before the app even reaches the review panel.
All of this is happening within a particularly demanding regulatory context in Europe, with regulations such as the Digital Services Act and the GDPR setting the pace. For users, this can translate into More notifications, more information in app listings, and more visible controlsFor developers, this means the need to assume that security is no longer a secondary issue.
Taken together, the 2025 data paints a picture in which Google has managed Block nearly two million problematic apps, clean up part of the developer ecosystem, and detect a large volume of threats outside the store.Malware and fraud on Android are far from gone, but the strengthening of controls and the intensive use of artificial intelligence are beginning to tip the scales, albeit slightly, in favor of defense.